Electric vehicles (EVs) have seen incredible growth over the last decade. While EVs were merely futuristic aspirations a decade ago, they have become an everyday reality for many people. Part of the reason EVs have seen such incredible growth is manufacturers’ investments in automation.
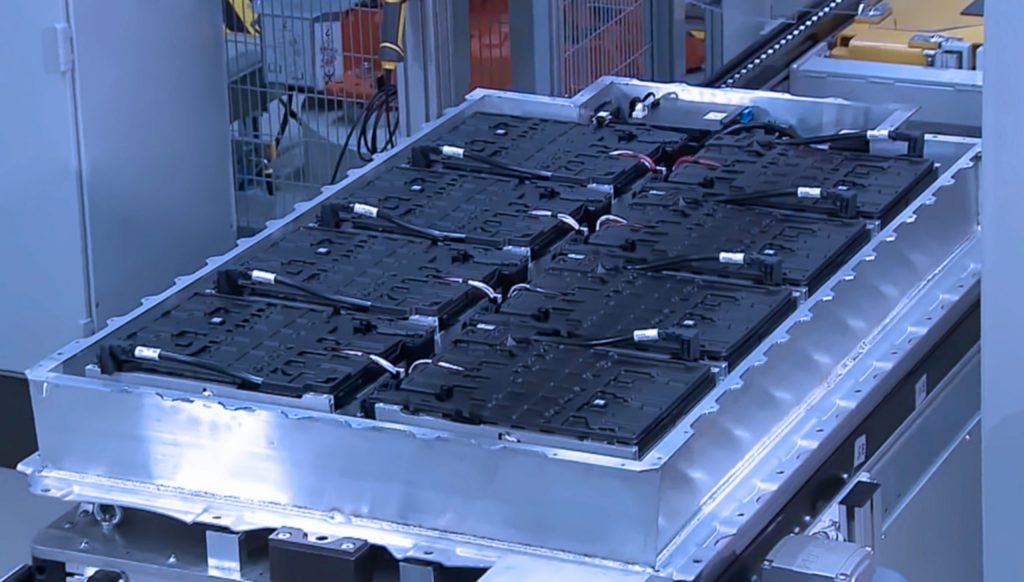

Given the relatively young age of many electric vehicle makers, they have invested in automation from the onset. Companies like Tesla have championed upfront investment in complex automation machinery, allowing them to scale their vehicle production.
However, electric vehicles are incredibly complex, involving thousands of components to create a finished car. Therefore, no one manufacturer can produce every component in-house. One such part that many EV manufacturers need to outsource is their battery tray.
In this blog, you’ll learn about the automated battery tray assembly process and about how +Vantage can help your business revolutionize its manufacturing processes.
Cell Bonding
Many battery cells have to be attached in cell stacks to supply the massive amount of electricity that an electric vehicle needs to function. However, the process cannot involve heat or excessive force because the cells are so delicate.
Therefore, battery manufacturers use adhesive bonding to join battery cells, creating a strong, flexible, and vibration-absorbing bond. To create a successful bond, manufacturers need an exact application of adhesive. Without a machine that can dispense the correct amount of adhesive and scan the application for errors, there can be dangerous consequences.
If the machine improperly applies adhesive, air pockets can occur. The air pockets could lead to poor insulation and a short circuit if the vehicle crashes. In such a high-voltage system, shorts could lead to disaster.
Battery Cell Stack Reinforcement
After the cells are bonded together, the stacks still need reinforcement to protect them and the driver in the event of a crash. Therefore, manufacturers need to install lateral braces around the stacks.
But, they have to do so without welding, as welding generates heat that can disturb the cells. To avoid such heat, manufacturers use a cold joining technique. In other words, battery makers need a mechanical joining process that will not disturb the cells. For that reason, self-pierce riveting is a popular joining technique.
Filling the Gaps
With the cells joined and secured, manufacturers need to ensure that the batteries operate within a specific temperature range. The batteries will overheat under load and fail without a robust temperature management solution. Therefore, they apply a heat-conducting thermal paste to transfer heat away from the cells and toward a heatsink.
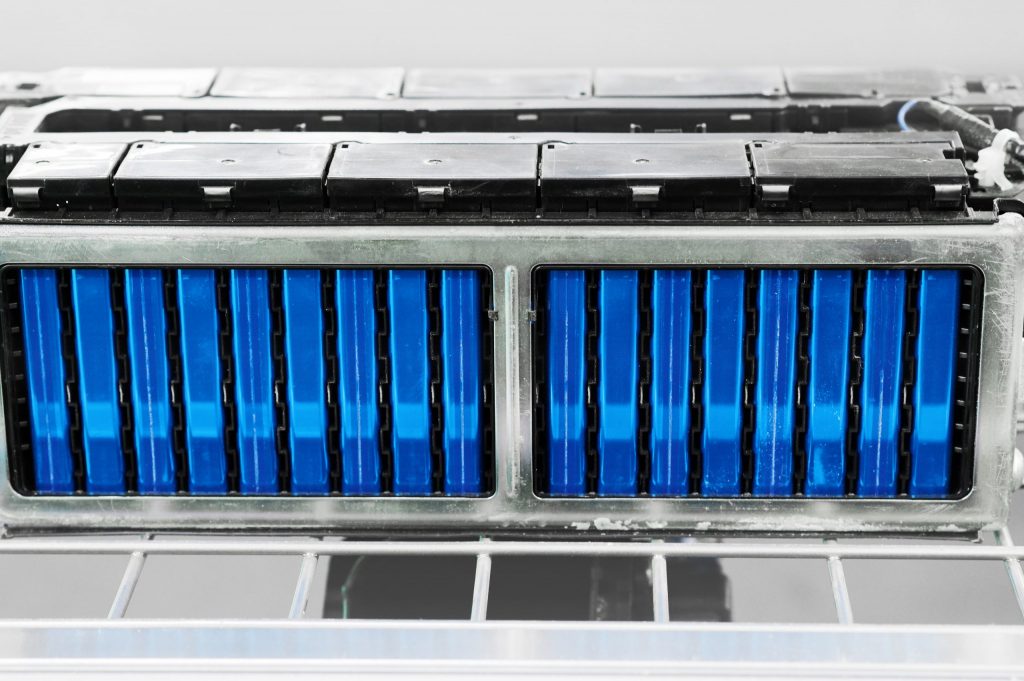

Manufacturers need precise metering technology to avoid bubbles that can cause temperature inconsistencies and catastrophic failure. Because of the high volumes of thermal paste necessary, a robust 3D scanning system is critical to application consistency and performance.
Battery Mounting
With the thermal paste gap filler applied, the battery modules must be mounted to their tray. However, the battery packs need to be tightened down with extreme accuracy to ensure that they contact the thermal paste in the tray without squeezing it out. Manufacturers need a precise tightening process to achieve even distribution and contact between the batteries and the thermal paste.
Battery Sealing
With the batteries tightened down to their tray, the next step in the car battery assembly process is to protect them from the elements. Without a robust sealing process, moisture can seep into the battery and cause corrosion. Corrosion can affect battery performance and lifespan, and cause danger to the vehicle’s passengers.
Therefore, battery makers need a precise and comprehensive sealing process for their battery assembly line. Because the battery still cannot handle high temperatures, the sealing process cannot involve excessive heat. Often, manufacturers use polyurethane, silicone, or butyl to provide a protective covering.
Joining Tray to Cover
The final step in battery tray assembly is joining the sealed battery tray to its cover. The cover provides the final layer of protection for the batteries, preparing them to be installed in the vehicles. The cover should be joined to the tray so that mechanics can remove it for maintenance.
Automating Your Manufacturing
Along every step of the battery assembly line, efficient manufacturers have invested in complex, robust automation technology. In addition, they have invested in systems that check for errors and quality at every step of the manufacturing process. With technology like 3D scanners, manufacturers can stop faulty components from reaching later stages of assembly and from endangering consumers.
However, battery tray manufacturers are not the only ones who benefit from automated manufacturing and quality control. Regardless of industry, manufacturers are investing in their technology to increase their production volume and quality.
If you want to learn more about how your business can benefit from +Vantage’s technology, click here for a free ebook that paints a picture of the products, services, and custom engineering we offer for our clients.



