Future Trends in Turnkey CNC Precision Manufacturing Work Cells
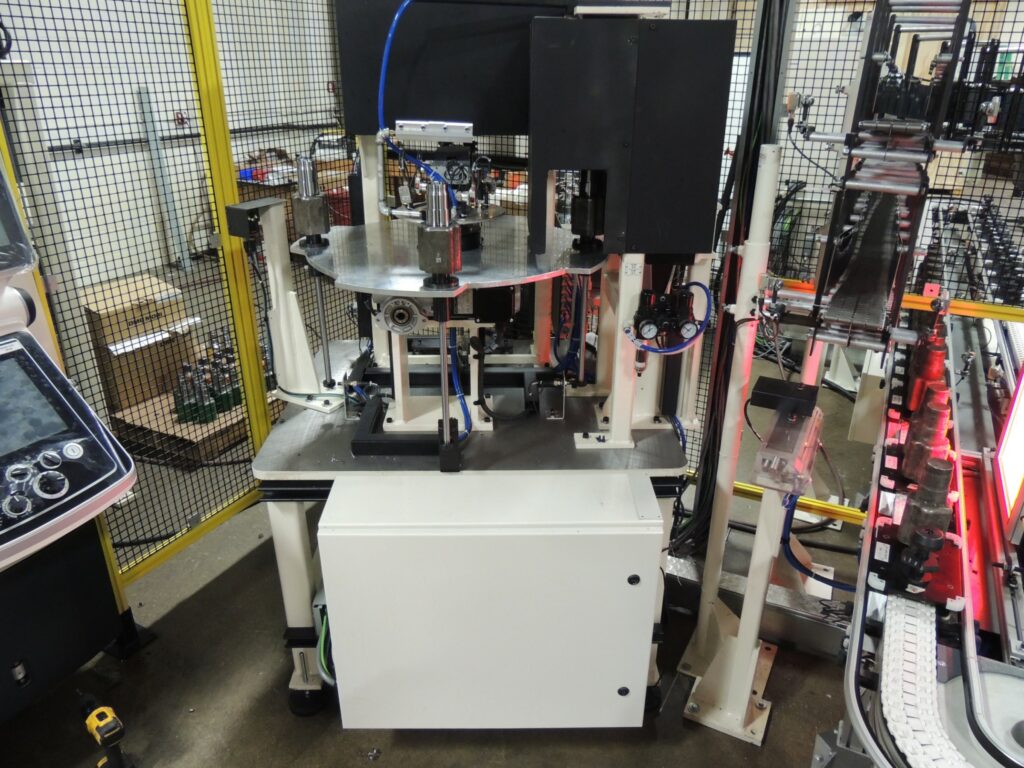 Machine tending automation, also called CNC (Computer Numerical Control) automation or CNC tending, is the process of using industrial and collaborative robots to load or unload machines. There are many benefits to this type of automation in manufacturing.
Machine tending automation, also called CNC (Computer Numerical Control) automation or CNC tending, is the process of using industrial and collaborative robots to load or unload machines. There are many benefits to this type of automation in manufacturing.
The rapid evolution of CNC precision manufacturing work cells plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing processes. Embracing innovation to drive efficiency, precision, and adaptability in manufacturing is crucial to staying competitive in the global market, and CNC automation can help companies do just that.
Let’s explore the current landscape, emerging trends, and future implications of turnkey CNC machining work cells for businesses.
CNC Machine Tending: The Current Landscape
The current manufacturing landscape is witnessing a significant shift toward automation, digitalization, and advanced technologies. CNC precision manufacturing work cells utilize cutting-edge technologies such as 5-axis machining, automated material handling, and advanced CAD/CAM software systems for companies to automate machine loading and unloading, taking this burden off employees.
The benefits of CNC tending include:
- Higher productivity
- Improved safety and accuracy
- Less downtime
- Reduced lead times
- Process repeatability and reliability for greater consistency
However, the limitations of current CNC manufacturing work cells include high initial capital investment, skill requirements for operation and programming, and limited adaptability to rapid changes in production demands. Fortunately, working with an experienced CNC integrator can help you overcome these challenges and leverage the full potential of precision robotic automation.
Latest Trends in CNC Technology
Advanced automation and robotics integration are driving the next generation of CNC manufacturing work cells. What does this mean for manufacturers?
Robotic Arm Integration for Enhanced Safety and Efficiency
Industrial robot arm tooling programmed for material handling, part loading and unloading, and even in-process quality control are increasingly being integrated into CNC work cells for repetitive tasks. This integration improves overall efficiency, reduces manual labor, and enhances safety in manufacturing environments.
Predictive Maintenance for Optimized Production
Digitalization and Internet of Things (IoT) integration in CNC work cells enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making. By connecting machines and processes through IoT sensors and data analytics, manufacturers can optimize production efficiency, monitor equipment health, and identify opportunities for process improvements.
Integrated Processes for Hybrid Manufacturing Solutions
Additive manufacturing integration is another emerging trend in CNC work cells. Combining subtractive CNC machining with additive manufacturing processes such as 3D printing allows for hybrid manufacturing solutions, enabling the production of complex, high-value parts with enhanced geometric freedom.
Integrated Gaging
Integrated gaging in CNC machine tending involves the incorporation of measurement and inspection systems directly into the CNC machine setup. This allows for continuous monitoring and adjustment of part dimensions during the machining process, ensuring high precision and quality control.
By seamlessly integrating gaging technology with the CNC machine, manufacturers can streamline production, reduce cycle times, and minimize the need for manual intervention. This advanced approach to machine tending enables real-time data collection and analysis, enhancing overall efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing operations.
Tool Compensation
Tool compensation refers to the CNC machine’s capability to automatically adjust tool offsets to account for variations in tool wear, temperature, and other factors that can affect machining accuracy.
By using sensor data and feedback from the machining process, the CNC machine can make real-time adjustments to the tool’s position and orientation, ensuring precise and consistent machining results. This feature is crucial for maintaining tight tolerances and high-quality production, as it allows for adaptive corrections without the need for manual intervention.
Manufacturers can minimize scrap, reduce downtime for tool changes, and increase overall productivity and part quality by incorporating tool compensation into the CNC machine tending process.
AI for Autonomous Decision-Making
AI and robotic machine learning applications are revolutionizing CNC manufacturing work cells by enabling predictive maintenance, adaptive process control, and autonomous decision-making. AI-powered algorithms can optimize tool paths, predict tool wear, and identify potential quality issues, leading to improved process efficiency and reduced scrap rates.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
Sustainability and green manufacturing are also driving the future of CNC work cells. Manufacturers are focusing on resource optimization and waste reduction by implementing lean manufacturing principles, recycling machining waste, and adopting energy-efficient processes to minimize their environmental footprint and reduce operating costs.
Future Implications and Industry Adoption
 The future of CNC machine tending lies in Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing. Integrating cyber-physical systems, IoT, and cloud computing will enable seamless communication and collaboration between machines, processes, and humans, leading to highly flexible and adaptive manufacturing systems.
The future of CNC machine tending lies in Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing. Integrating cyber-physical systems, IoT, and cloud computing will enable seamless communication and collaboration between machines, processes, and humans, leading to highly flexible and adaptive manufacturing systems.
Industry 4.0 will transform traditional factories into smart ones, where interconnected machines and systems can communicate and coordinate production processes autonomously, improving productivity, quality, and agility. Adopting Industry 4.0 principles in CNC manufacturing work cells will enable real-time production monitoring, predictive maintenance, and agile reconfiguration of production lines to meet changing demands and improve resiliency.
The potential opportunities associated with the future of CNC integration are significant. Adopting advanced technologies and digitalization will enable manufacturers to address the challenges of customization, mass production, and rapid product development. However, there will be a need to upskill the workforce to operate and maintain these advanced manufacturing systems.
The shift toward sustainable and green manufacturing practices will also drive innovation in material science, recycling technologies, and energy-efficient processes for even more cost savings.
Download the RōBEX Brand Guide: Automation Made Seamless
The industry’s adoption of robots for machine tending automation will revolutionize how products are manufactured. Manufacturers who embrace these future trends will be well-positioned to stay competitive in the global manufacturing landscape.
Are you ready to discover more about how RōBEX can help you successfully integrate robotic automation into your processes? Learn about how we can help you by downloading your free copy of our Automation Made Seamless eBook.